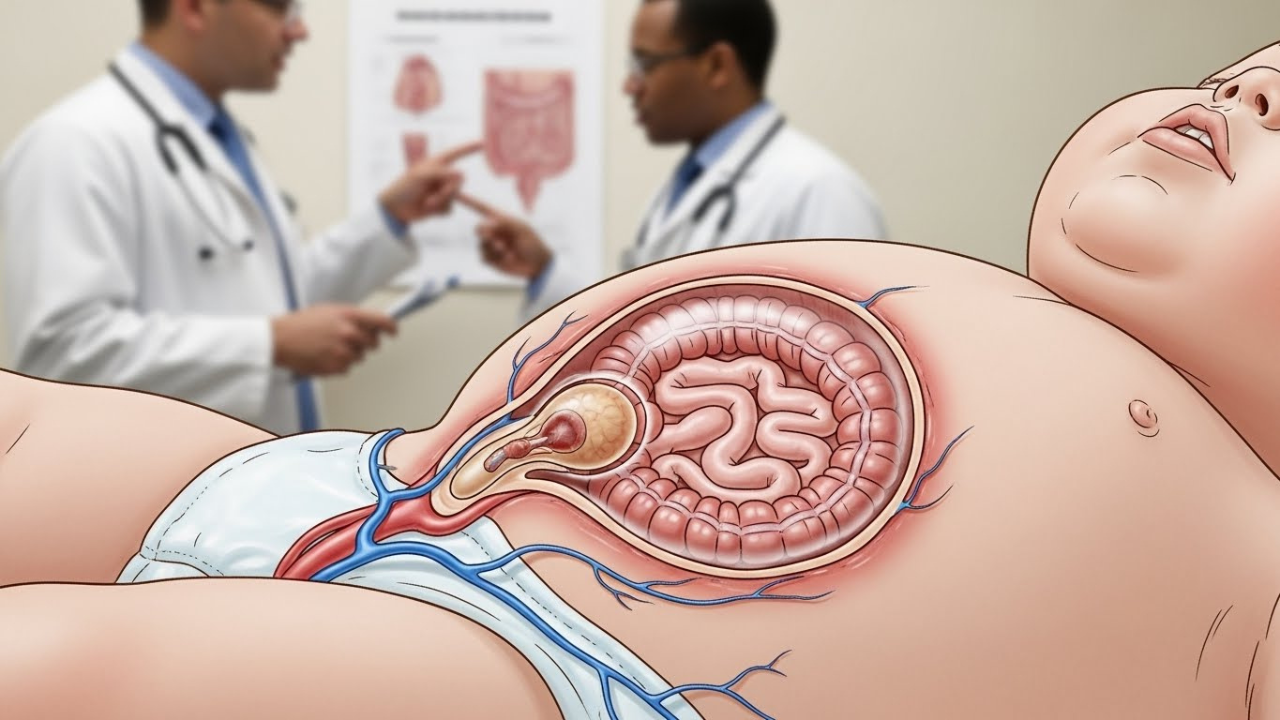
Gastroshiza might not be a term you hear every day, but it’s a condition that affects many families around the world. This congenital defect occurs when an infant’s abdominal wall doesn’t fully close during development, causing internal organs to protrude outside the body. Though it can sound alarming, understanding gastroshiza is crucial for expectant parents and caregivers alike. In this blog post, we’ll dive into what gastroshiza is all about—its causes, symptoms, treatment options, and how to manage life after diagnosis. Whether you’re seeking information out of curiosity or necessity, you’re in the right place to learn more about this condition and its implications for those affected by it.
What is Gastroshiza?
Gastroshiza is a congenital defect that occurs when the abdominal wall fails to close completely during fetal development. This results in the baby’s intestines, and sometimes other organs, protruding outside of the body.
Unlike similar conditions such as omphalocele, where organs are covered by a protective sac, gastroshiza exposes these organs directly to the environment. This can lead to various complications shortly after birth.
The exact cause of gastroshiza remains unclear, but it’s believed that genetic and environmental factors may play a role. The condition typically appears more frequently in males than females and is often detected through prenatal ultrasounds.
While this diagnosis can be daunting for parents-to-be, understanding gastroshiza helps pave the way for effective treatment options right from birth.
Causes of Gastroshiza
Gastroshiza occurs when a baby’s abdominal wall doesn’t close properly during development. This defect allows the intestines to protrude outside the body.
The exact cause remains unclear, but several factors may contribute. Genetic predisposition plays a role, as some families have a history of this condition. Environmental influences also come into play.
Certain maternal health issues can increase risk factors for gastroshiza. For instance, young maternal age and smoking during pregnancy are linked to higher occurrences of this defect.
Nutritional deficiencies in expectant mothers might impact fetal development as well. Specifically, lack of essential vitamins or minerals could hinder proper formation of the abdominal wall.
Researchers continue to investigate these causes further, aiming to understand how different elements interact in triggering gastroshiza.
Symptoms of Gastroshiza
Gastroshiza presents itself with distinct symptoms that can vary among individuals. One of the most noticeable signs is the protrusion of abdominal organs outside the body through an opening in the abdominal wall. This condition typically manifests at birth.
Parents may observe a clear, thin membrane covering these exposed organs. Sometimes, this membrane may not be present, leading to direct exposure to air and environmental factors.
Infants with gastroshiza might also experience feeding difficulties due to their unique anatomical situation. Gastrointestinal issues like vomiting or difficulty digesting food can arise as well.
Breathing challenges are another concern; some babies may struggle due to pressure from external organs on their diaphragm. Early recognition of these symptoms is crucial for timely medical intervention and support.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options
Gastroshiza is typically diagnosed through prenatal ultrasounds, which can reveal the condition before birth. After delivery, a physical examination confirms the diagnosis. Doctors look for external organs protruding from the abdominal wall.
Treatment options depend on the severity of gastroshiza. Surgical intervention is often necessary to place the exposed organs back into the abdomen. This procedure usually occurs shortly after birth and aims to protect these vital structures.
In some cases, doctors may use a technique called silo placement initially. This involves inserting a protective covering over the herniated organs and gradually moving them back inside as swelling decreases.
Post-surgery, ongoing care includes monitoring for potential complications such as infections or bowel obstructions. Pediatric specialists will play an essential role in managing recovery and ensuring proper nutrition during this critical time.
Long-term Effects and Complications
Gastroshiza can lead to various long-term effects and complications. One of the most significant concerns is nutritional deficiency. Since the intestines may not function optimally, affected individuals might struggle with absorbing essential nutrients.
Additionally, there is a risk of intestinal obstruction. Scar tissue from surgeries or damage could narrow the passageway in the intestines, causing pain and requiring further medical intervention.
Growth and developmental delays are also common among children born with gastroshiza. These kids may face challenges that affect their physical growth as well as cognitive development.
Psychosocial aspects shouldn’t be overlooked either. Children dealing with visible scars or ongoing health issues might experience anxiety or social withdrawal due to their condition.
Regular follow-ups with healthcare providers are crucial for monitoring these potential complications, ensuring timely interventions when necessary.
Lifestyle Changes to Manage Gastroshiza
Managing gastroshiza often requires significant lifestyle adjustments. A balanced diet is essential. Nutrient-rich foods can aid in recovery and overall health. Focus on fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains.
Hydration plays a crucial role too. Keeping well-hydrated helps maintain bodily functions and supports digestion. Aim for at least eight glasses of water daily.
Regular check-ups with healthcare professionals are vital. These visits ensure that any complications are monitored closely and addressed promptly.
Incorporating gentle exercise can also be beneficial. Activities like walking or swimming may improve physical strength without straining the body.
Emotional well-being shouldn’t be overlooked. Engaging with support groups or mental health professionals can provide comfort during challenging times. Connecting with others who face similar challenges fosters resilience and hope.
Coping with a Diagnosis and Support Systems
Receiving a diagnosis of gastroshiza can be overwhelming. It’s normal to feel a mix of emotions, from fear to confusion. The journey ahead may seem daunting.
Connecting with support systems is crucial. Family and friends can provide comfort during challenging times. Don’t hesitate to share your feelings with them; open communication fosters understanding.
Consider joining support groups where you can meet others facing similar challenges. Hearing their stories might offer insights and reassurance that you’re not alone in this journey.
Healthcare professionals also play an essential role in coping strategies. They can guide you through treatment options and answer questions about living with gastroshiza.
Remember, each day is a step forward, whether big or small. Focusing on the present moment helps ease anxiety about the future while building resilience for what lies ahead.
Conclusion
Gastroshiza is a rare birth defect that can have significant implications for those affected. Understanding the condition is crucial for managing it effectively. From its causes and symptoms to available treatment options, being informed empowers families and patients alike.
The journey doesn’t end with a diagnosis. Long-term effects may arise, necessitating ongoing care and support systems. Lifestyle changes can help manage some challenges associated with gastroshiza, promoting better health outcomes.
Emotional support plays an essential role in navigating this complex condition. Connecting with others who understand the experience can provide comfort and strength along the way.
Awareness of gastroshiza fosters a more compassionate society where individuals receive the understanding they need as they navigate their unique journeys.